Electrical resistance of human body has been estimated to be 1,000 Ω according to IEEE Std. 80 standard. Resistance is the value from hand-to-feet and from hand-to-hand or from foot to foot. IEC60479-1 standard indicates that human body resistance is a function of contact voltage and may lead to less than the fixed value of 1,000 Ω recommended by IEEE Std. 80.
IEEE 80 is the guide for safety in AC substation grounding. IEC 60479-1 provides guidance on the effect of current on human beings and livestock.

Resistance of internal human body is approximately 300 Ω whereas body resistance including skin range from 500 Ω to 3,000 Ω [Ref 1]. Any cuts or bruises on the skin will cause further reduction in body resistance. Reference [1] is a classic paper on electrical tests carried out on humans under various conditions. Men typically have lower electrical resistance than women. Parameters that can affect body resistance are skin surface salt content (sweat) and moisture. At voltage above 500V skin can break down quickly, exposing the internal issue which has lower resistance than skin. Electrocution at high voltage often only show pin head size entry and exit wounds but can result in large internal current flow and causes deep tissue and muscle injury. AC voltage is also more dangerous than DC voltage.

Read: Step and Touch Potential
Body resistance and applied voltage has a direct impact on how much electric current passes through the body during electric shock condition. Lower the body resistance and larger the voltage, greater the current flow and greater will be the damage to tissues, muscles, and nerves. Death due to electric shock is known as electrocution.
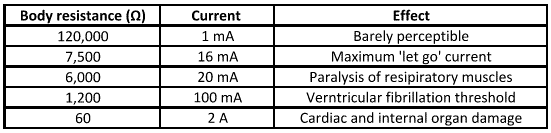
How to increase human body electrical resistance?
The internal body resistance is around 300 Ω and it’s the skin that offers most electrical resistance to flow of current. A dry calloused skin may have resistance of more than 100,000 Ω and a moist and sweaty skin will have much lower value.
Other than keeping the skin dry, there is nothing much we can do to increase body resistance. This is where personnel protective equipment (PPE) comes in to our aid. Specifically, voltage rated gloves and EH rated shoes provide the most protection from a shock hazard by increasing the contact resistance at the hand and the feet.

Voltage rated gloves are available in different voltage classes and depending on the application, appropriate glove may be chosen. For 120V applications it is common to use Class 00 gloves which are rated for 500VAC or 750 VDC maximum. Class 00 gloves can be used up to 1000VAC or 1,500VDC maximum.
Read: Ghost or Phantom voltage
Electric hazard [EH] rated shoes are specifically designed to impede the flow of electricity from shoe to ground. In other words, EH rated shoe adds significant resistance to the flow of current.
Read: Substation grounding: Role of crushed rock
Summary:
Resistance of human body is estimated to be 1000 Ω.
Resistance will vary when the skin surface has salt content from sweat etc.
Resistance will vary when the skin surface is moist.
Resistance will vary when the skin has cuts or bruises.
Lower body resistance can lead to larger current flow and electrocution.
Using voltage rated gloves and EH rated shoes help increasing effective body resistance to electric current.
Read: Stray voltage, How does it originate?
Reference [1]: Effects of electric shock on man, Charles F Dalziel
Reference [2]: Conduction of Electrical Current to and Through the Human Body: A Review, Raymond M. Fish and Leslie A. Geddes
