Potential Transformer ratio is the ratio of the primary rated voltage of the PT divided by the secondary rated voltage of the PT. A 480:120V rated PT will have a PT ratio of 4.
How is the PT ratio calculation or VT ratio calculation performed when the rated PT primary voltage is different from the voltage at which the PT is applied? Often, the primary rated voltage of the PT might be different from the system voltage at which the PT is applied. The rating of the potential transformer primary must be same or higher than the system voltage at which PT is applied. For example, a 600V:120V rated VT can be applied on a 440V rated bus without any problem.
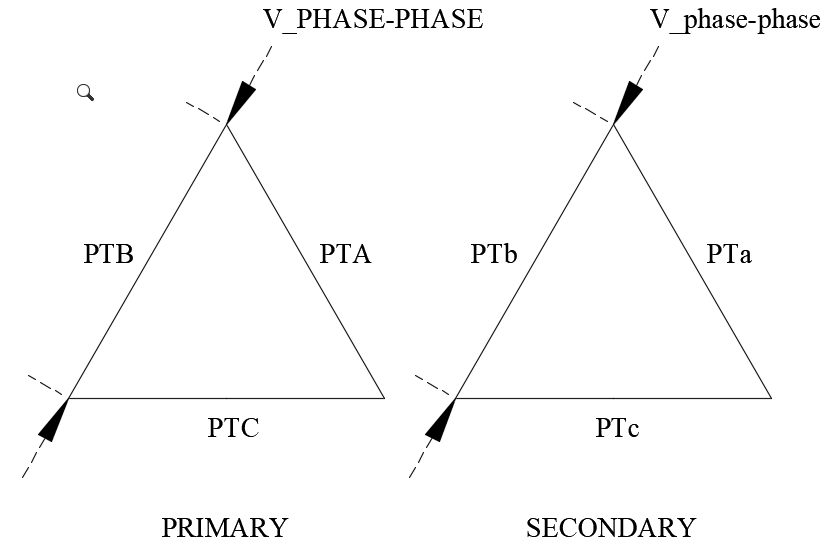
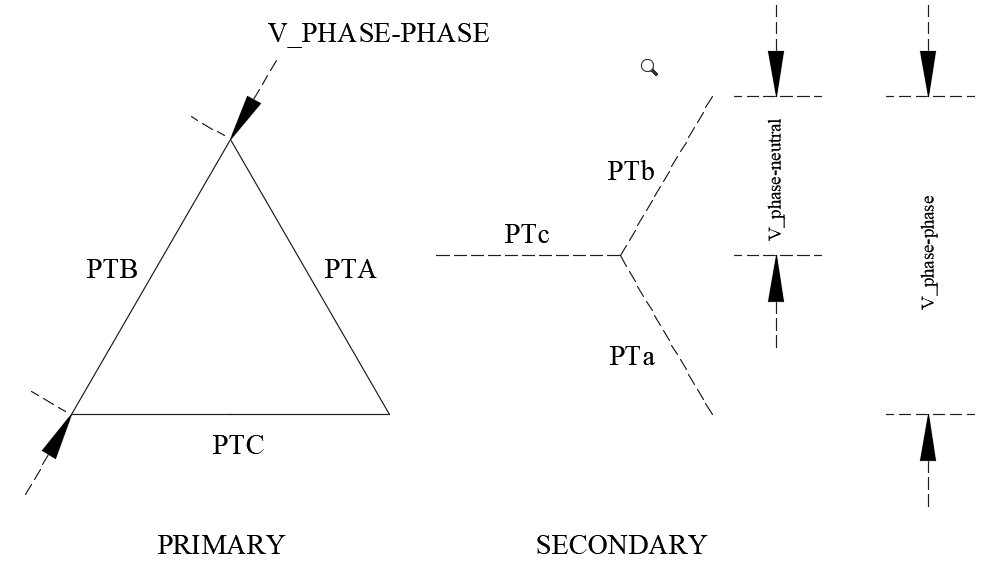
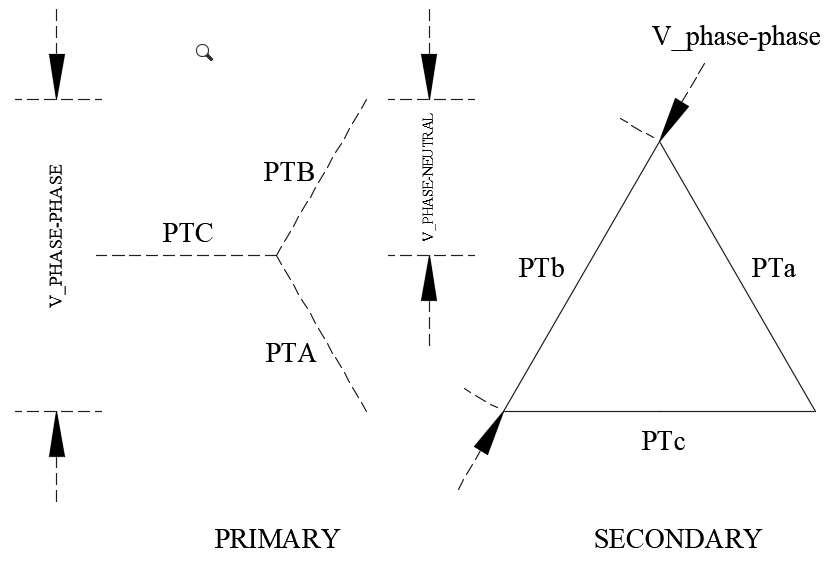
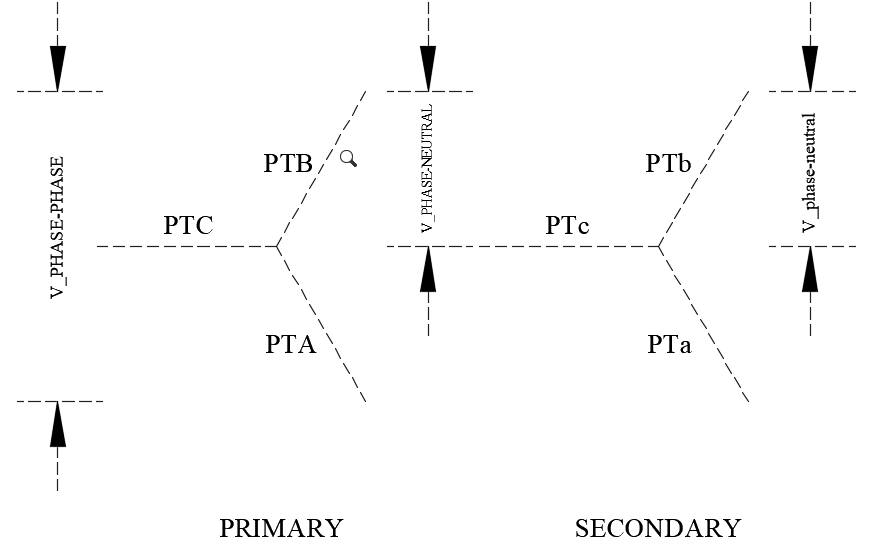
When potential transformers are applied at a voltage different from its rated voltage, the secondary voltage needs to be calculated. In addition, for a three phase PT connection, individual PT could be connected in delta, open delta or star (wye) connections. When programming modern digital relays it is necessary to input the expected PT secondary voltage. Relay may need the phase-phase secondary voltage or phase-neutral voltage depending on the type of relay.
Potential Transformer ratio calculation can be performed using the calculator below for a range of three phase connections as well as single phase connections. User can determine the PT secondary voltage when connected in star (wye) or delta.
Note: PT and VT refer to the same when referring to instrument transformers used for metering, relaying though VT is the new terminology.
Other Articles:
Voltage Transformer Accuracy Classes
Transformer Connections: Phase Shift and Polarity
