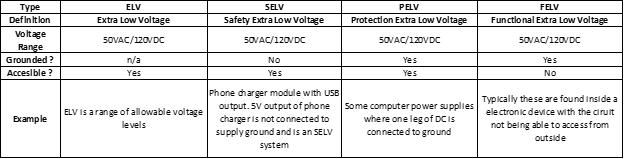
ELV stands for Extra Low Voltage and is indicative of systems operating under 50VAC or 120VDC (ripple free). ELV systems operate at low enough voltage that operational safety is improved. Common building management systems such as CCTV, card access, security system etc. are all examples of ELV installations. For ELV systems, fault protection may not be needed as under certain conditions basic protection is provided by limitation of voltage.
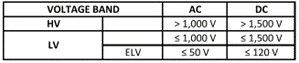
IEC defines different types of ELV systems depending on the type of grounding and other considerations. These are commonly known as SELV, PELV and FELV systems.

Read: Ghost voltage
SELV
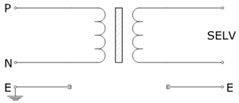
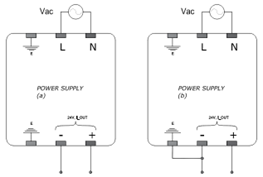
SELV stands for Safety Extra Low Voltage or Separated Extra Low Voltage is a system in which voltage does not exceed ELV voltages (50VAC or 120VDC) under fault or earth fault conditions in other circuits. Key features of SELV systems are:
- Voltage that does not exceed 50VAC or 120VDC so that shock hazard is very low. In more demanding areas this can even be 25VAC or 60VDC.
- No intentional connection of any live conductor to earth (ground) is permitted.
- SELV voltage cannot exceed the ELV limits under normal or fault conditions including earth fault in other circuits.
- SELV sockets or plugs do not have ground connection to prevent accidental grounding of live terminal.
- Double or reinforced insulation or protective screening from other circuits that carry higher voltage.
- SELV circuits are not installed in the same conduit as other high voltage circuits.
- Separated from other live circuits (other than SELV and PELV) by a distance atleast equal to distance between terminals of isolation transformer.
- Simple separation from other SELV and PELV systems.

By not referencing to ground (earth), risk of accidental shock hazard is avoided as there is no path for current to flow through the human body to ground. Presence of reinforced insulation and segregation from other high voltage circuits make SELV a safe approach to power ELV circuits. Additional details of SELV systems can be obtained from IEC 61140.
Read: Resistance of human body
SELV sources can be an isolation transformer, motor-generator, electrochemical battery. SELV source can also be an electronic power supply confirming to standards and in the event of an internal fault, the voltage at the terminal does not exceed the SELV voltage limits. Care should be taken when two DC power supplies are connected in series as the combined voltage may exceed the SELV requirements of maximum 60VDC.
Read: Stray Voltage- How does it originate?
Common 24VDC and 48VDC power supplies fall within the SELV voltage limits when there is no intentional connection of live conductor to ground (earth). Examples of SELV sources are many computer power supplies, landscape lighting, hand tools, CCTV, Access controls etc.
PELV
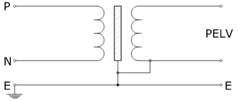
PELV stands for Protection Extra Low Voltage is a system in which voltage cannot exceed the ELV limits under normal conditions and under single fault conditions except earth faults in other circuits. Nominal PELV voltage should not exceed ELV limits of 50Vac rms or 120VDC when used in dry locations. PELV sources can be an isolation transformer, motor-generator, electrochemical battery. PELV source can also be an electronic power supply confirming to standards and in the event of an internal fault, voltage at the terminal does not exceed the PELV voltage limits.
Read: Isolated Power Receptacle
Key features of PELV systems are:
- Voltage that does not exceed 50 Vac rms or 120VDC (ripple free) when used in dry locations and when large area contact of live parts with human body is not expected. In more demanding areas this can even be 25VAC or 60VDC.
- In areas where the above dry location condition cannot be satisfied, the limits are 6 Vac rms or 15VDC.
- PELV voltage cannot exceed the ELV limits under normal or fault conditions except for earth fault in other circuits.
- Intentional connection of one live conductor to earth (ground) is required.
- PELV sockets or plugs shall not allow connection to other systems such as SELV.
- Double or reinforced insulation or protective screening from other circuits that carry higher voltage.
- Simple separation from other systems that carry higher voltage.
Read: Power Quality checks using a multimeter
FELV
FELV stands for Functional Extra Low Voltage is a system which does not meet the requirements of SELV or PELV circuits. Voltage range for FELV is the same as that for SELV and PELV with the difference that the insulation between live conductors and other circuits are less than basic insulation used for SELV and PELV. Unlike SELV or PELV, FELV does not have double or reinforced layer of insulation between ELV output and mains input. Like PELV, one conductor is connected to earth for reference. FELV circuits are often inside another device that is not accessible from outside such as LED light tapped off from mains supply or relays, contactors, transformers that are not sufficiently insulated from neighboring high voltage circuits.