Capacitor trip device [CTD] or capacitor trip unit [CTU] is a device that provide DC source of energy for circuit breaker tripping or closing when normal AC or DC control power is lost. CTD converts AC voltage in to DC by half-wave or full-wave rectification. Capacitor will be charged to DC voltage corresponding to peak of AC wave which is then used as a ‘reservoir’ when normal AC control power is lost. Capacitor trip device can also be used with DC input voltage in which case capacitor will be charged to the value of DC input voltage.
Capacitor trip devices are commonly used in switchgear to provide trip circuit power and to provide voltage sag ride through capability for digital relays. CTD is not commonly used for closing applications as it is expected that the normal control power will be available when closing is desired.

CTD can be wired to trip coil, lockout relay, any relay that accepts DC control voltage. Capacitor size should ideally be selected so that it forms a tuned circuit with the inductance of the trip coil solenoid. CTD may not be used as a continuous source of DC power except under limited circumstances as discussed later in this article.
Link to: Capacitance calculator
CTD capacitance could be anywhere from 330uF to 4500uF with larger capacitance translating in to more stored energy and more trip operations. When AC input is lost, DC power is immediately available to load as there are no relays or switches in CTD. On initial energization, DC power is immediately available even before capacitors are fully charged. Capacitors are typically charged to 90% voltage in less than 0.5s when CTD is turned ON from a discharged state.
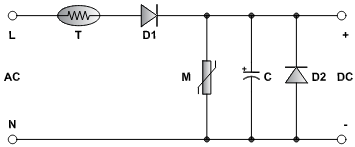
In figure 2, Thermistor ‘T’ is used to protect against short circuits and overloads. Diode ‘D1’ performs half-wave rectification along with capacitor ‘C’. MOV ‘M’ provides surge protection on the AC side whereas reverse connected diode ‘D2’ provides surge suppression on the DC side.
Types of capacitor trip device
Half-wave rectified CTD: Half-wave rectified CTD is more common as they are cheaper in addition to the availability of common neutral between AC and DC side which simplifies control wiring.
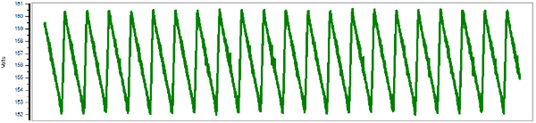
Half-wave rectification only converts one half of AC cycle in to DC leading to larger DC voltage ripple. Ripple voltage is not a problem for inductive load like trip coil. Only when CTD is used to provide continuous DC power, ripple will be present. See the ripple voltage in figure 4 where a 330uF CTD is used to power 24VA resistive load while the AC input is still healthy.
Under rare conditions where CTD is used as part of control schematic (like figure 6) DC ripple may affect the operation of sensitive digital relay inputs or relay power supply.
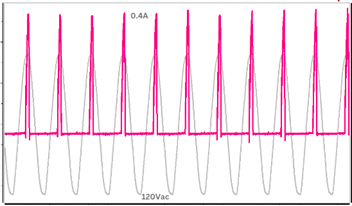
Figure 5 shows AC input current in to CTD when relay is used to continuously power a protection relay. Note the AC current is drawn in pulses every positive cycle due to half-wave rectification.
Full wave rectified CTD
CTD with full-wave rectification rectifies both positive and negative half cycle of AC. Full wave rectification provides DC voltage with less ripple compared to half wave rectification. However, these CTD lack common neutral between AC and DC side and is more expensive compared to half-wave rectified CTD. For most circuit breaker trip circuit applications, reduced ripple do not bring any added advantage. Full-wave rectified CTD can be used where separation between AC and DC side neutral and reduced DC ripple is desired. Some vendors have full wave rectified CTD with battery backup that can hold charge for three days or more.
Read: Open neutral: voltage fluctuation and stray voltage
Available Energy of CTD
Manufacturers provide the energy available from CTD in joules (J):
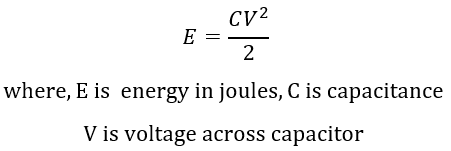
Voltage on capacitor will be the peak voltage of input AC waveform. For 120VAC input, output voltage will be 120*sqrt (2) = 120*1.414=169VDC. For DC input CTD, output voltage will have the same magnitude voltage as input.
Can CTD be used as a DC power supply?
A common misapplication is to use CTD as a DC power supply since the output is DC (170VDC or 340VDC etc.). Many manufacturers do not recommend using CTD as DC power supply. Newer CTD’s however can support a small continuous load (2VA-20VA or more)which may be specified in the data sheet or can be obtained from manufacturer. Higher continuous DC load will cause higher AC current draw causing input thermistor (see figure 2) heating and increased thermistor resistance. Increased thermistor resistance will eventually reduce DC output voltage as load is increased.
CTD may be used to provide DC control power to digital relays as CTD can provide short term (few cycles to few seconds) voltage sag ride through support.

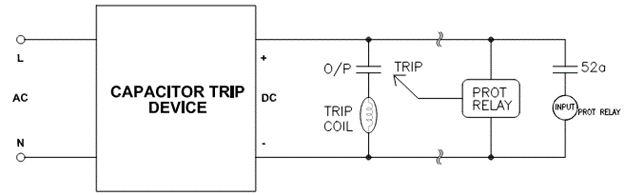
Where CTD is applied as DC source, it is often done for economic reasons as providing reliable control power in switchgear involves installing UPS or having station DC power supply. When AC control voltage sags (due to faults etc.) digital protection relay may shutdown or malfunction. By having a CTD power the relay as shown in figure 6, AC voltage sag will not affect relay operation for few seconds. If the relay must initiate a trip, it can successfully do within this time frame. Status inputs such breaker status (52a) wired to relay input can also backed up by CTD. CTD output should not be paralleled with other CTD.
Read: Voltage sag due to induction motor starting
How long CTD can provide backup power?
When AC supply is lost, capacitor provides DC power to the load. How long this power is available depends on the following parameters:
- Initial voltage [V0] on the CTD capacitor
- Drop out voltage [V] of the connected device
- Capacitance of CTD [C]
- Resistance of load [R]
Time for discharge in seconds [t] can be calculated as:
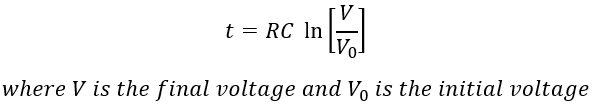
Table 1 lists examples of trip and close solenoid DC resistance. Table 2 lists the control voltage range.
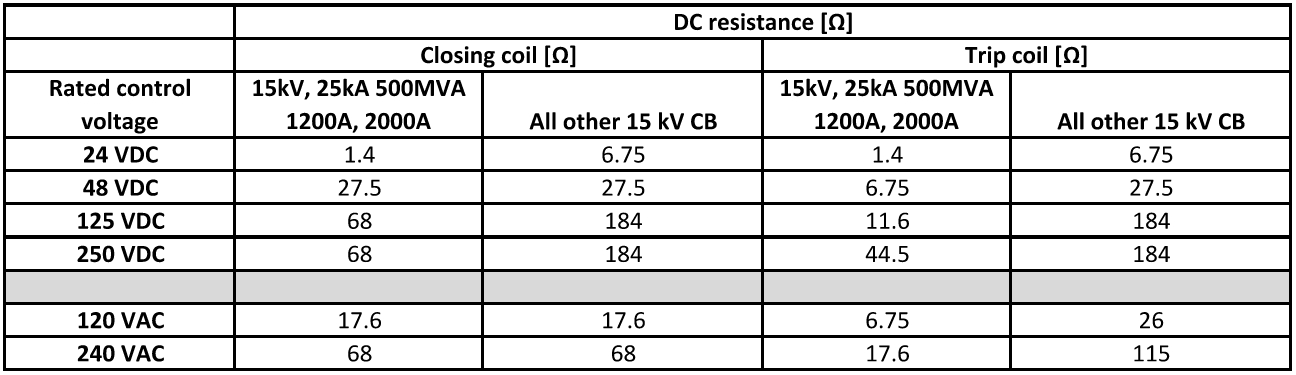
For most applications, trip coil only need to be energized for ~ 15ms and close coil for 20-25ms meaning CTD will have energy to perform multiple trip operations. For a given trip time, energy equation and the equation above can be used to iteratively derive the number of trips that a given CTD can provide. Table below can be used to estimate the low end ‘drop out’ voltage of a DC trip coil if actual data is not available. This table also provides the AC control voltage range.
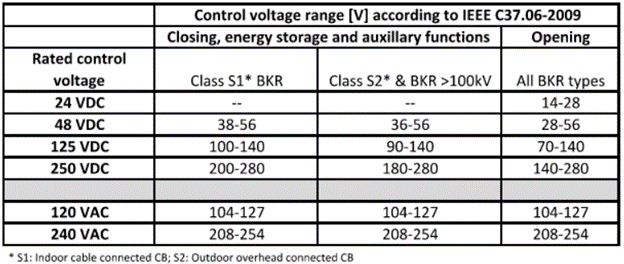
For selecting appropriate voltage ratings for CTD, IEEE Std. C37.06 standard section 10 ‘Control voltage ranges for circuit breakers’ may be referenced. As an example, 125VDC rated trip coil is frequently applied with 120VAC CTD which have no load output voltage of 170VAC. At the outset, output voltage may appear high but the real reason is that CTD has to reliably trip the circuit breaker with a wide AC voltage range of 104V-127V. Variation can happen due to utility voltage tolerance or facility loading.
Read: Voltage swell due to line-ground fault
CTD hold charge for a long time (10’s to 100’s of minutes) under no load. Duration is determined by self-discharge through capacitor’s internal resistance.
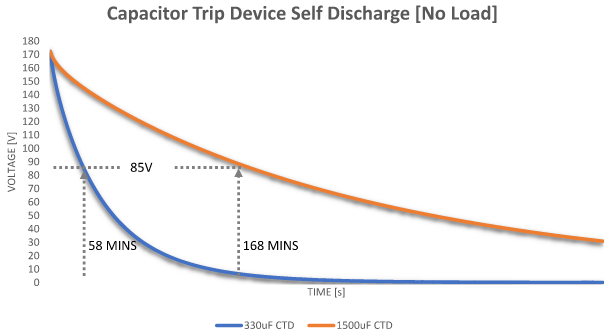
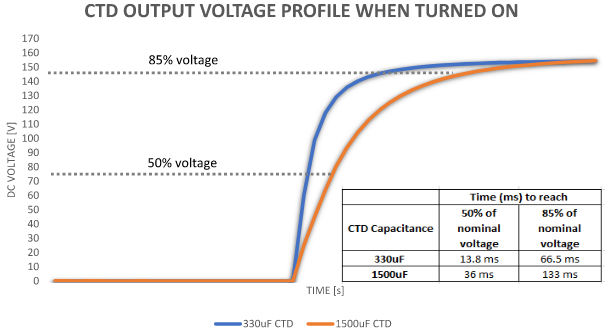
Figure 8 shows self-discharge voltage profile for two different CTD, one with 330uF and another with 1,500 uF capacitance. Time to reach 85VDC (50% of nominal) is measured as 58 minutes and 168 minutes respectively. Self-discharge time can vary between manufacturers depending on the quality of capacitor used.
CTD inrush current
When CTD is energized from a zero energy state, there will be inrush current that is only limited by input thermistor.
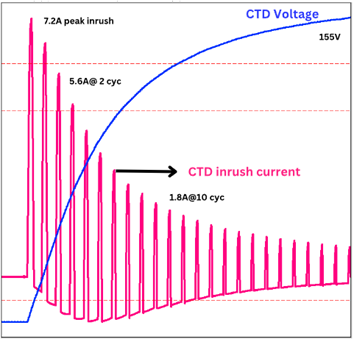
Properly rated AC circuit breakers or fuses are necessary to prevent nuisance trips. When there are multiple CTD in switchgear, energizing will cause large current draw. Since CTD conducts at the peak of AC cycle, worst case peak can be approximated by multiplying the peak current of an individual CTD with the number of CTD in the circuit. When there are many (>10) CTD in control circuit, it may be beneficial to distribute half on either side of the center tapped control power transformer thus avoiding overloading one phase and provide better control voltage stability during turn on.
Read: Difference between control power transformer and potential transformer
Discharging capacitive trip device
When control wiring needs troubleshooting it is important to discharge CTD in the circuit to avoid shock hazard. Large capacitors can hold lethal charge to injure or cause electrocution.
Read: What is the Electrical resistance of human body?
CTD can be discharged by connecting a 5 watt, 500 Ω resistor across the output terminals.
