Harmonic voltage and current present in power system can negatively affect the quality of reception of telephone and other communication circuits. Harmonics generate interference through inductive coupling from power lines to communications lines. Telephone Interference Factor [TIF] is a factor proposed in IEEE 519-2014 standard as measure of audio circuit interference caused due to harmonics in electric power system. TIF accounts for the fact that audio interference is a function of both amplitude and frequency of harmonics. Phasing out open wire telephone lines has minimized the interference issues in recent decades.

Power system harmonics encompass wide range of frequencies from low 100/120Hz to 3 kHz or more. Of these frequencies, interference caused by each harmonic frequency will be different due to audio frequency perception variation of human ear and frequency response of telephone or communication system. IEEE519-2014 standard provides weighing functions at various frequencies to account for coupling between harmonic frequencies and telephone circuits as well as sensitivity of human ear at those frequencies. Weights are assigned based on the amount of disturbance produced relative to that produced by a 1,000 Hz signal similarly injected.
Lower order power harmonic frequencies are imperceptible to human ear while higher order harmonics fall in to low-audio range. Zero sequence current harmonics (9th and higher multiples) cause significantly more interference than positive and negative sequence harmonics. This is because zero sequence harmonics are additive and do not decay as rapidly with distance.
Read: Positive and zero sequence impedance of cable
TIF can be voltage TIF or current TIF. TIF is a dimensionless quantity. Formula for telephone interference factor is given by:
![TIF weighting values [IEEE 519-2014]](https://voltage-disturbance.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Picture1-1.png)
Serious telephone interference is usually caused due to some higher order harmonic resonance. Notice from the TIF weighting curve that higher order harmonics are weighted heavily meaning these frequencies tend to cause more interference in the audio range. Locations near devices that ‘sink in’ zero sequence current such as harmonic filter banks and star connected grounded capacitor banks may experience higher levels of TIF. Adjusting the tuning reactor will usually move resonance out and remove the interference issue.
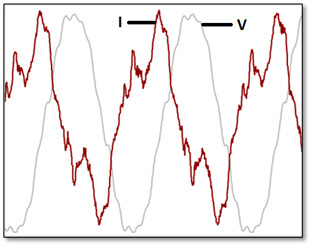
I-T Product
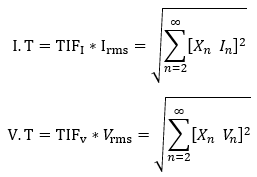
Telephone interference factor is often expressed as a product of current and TIF and this is known as I-T product. I is the rms current in amperes and T is the TIF. TIF can also be expressed as product of voltage and TIF and is known as V-T product.
IEEE 519-2014 standard provides guidelines on I-T values for distribution systems operating less than or equal to 34.5kV. Standard states that these guidelines should not be considered as recommended limits due to wide range of variability in the system.

Additional information on the I-T guidelines can be found in IEEE 519-2014 standard.
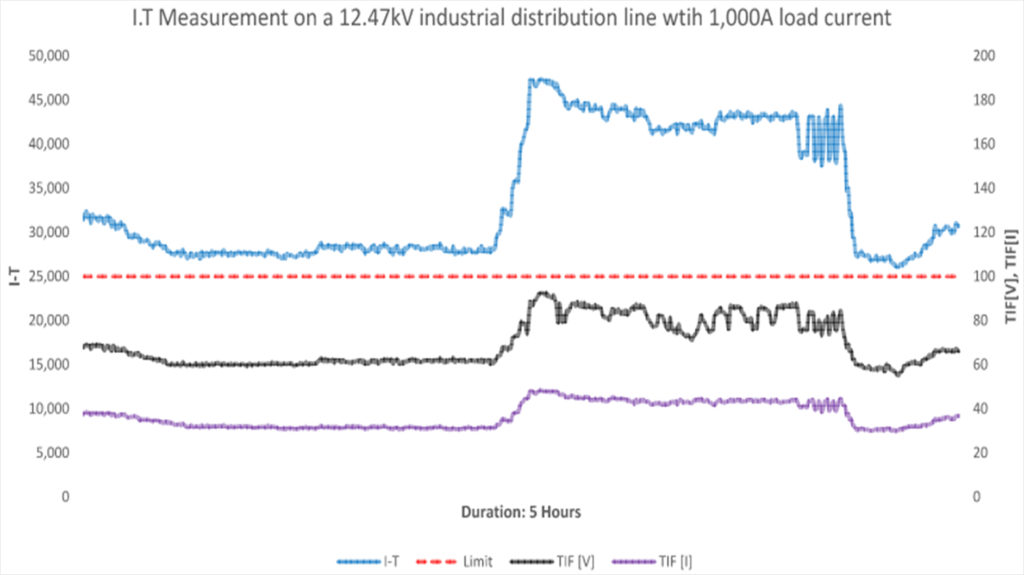
Figure 4 shows the I-T, TIFv, TIFi example measurement results from a large industrial site with extensive overhead distribution at 12.47kV system voltage. This site has I-T product consistently exceed the IEEE limit (guideline) values of 25,000 which is classified as ‘Levels that probably will cause interference’.
Summary
Telephone Interference Factor [TIF] is a measure of interference caused by power system harmonics in the audio range. Details of TIF calculation are given in IEEE 519-2014 standard. TIF calculation give different ‘weights’ based on perception of human ear to different harmonic frequencies. TIF can be calculated for voltage or current though telephone interference is primarily caused by inductive coupling due to harmonic current flow.
Similar in concept to TIF, standard also defines I-T and V-T product which is TIF multiplied by rms current or voltage. Standard gives guideline on thresholds above which interference is more likely.
Telephone signals are no longer carried over open wire lines and this has made TIF less of a concern. TIF is a parameter that is available in many popular power quality meters as a standard metering parameter. TIF may be used as a general check on interference issues in the low audio frequency range and if thresholds are exceeded then more sophisticated measurements can be carried out.
