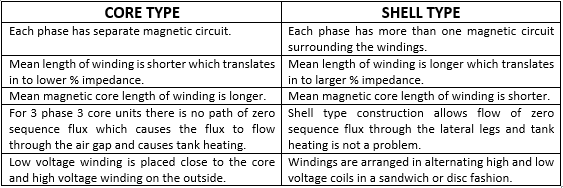
Power Transformers can also be classified according to the type of construction: Core Type and Shell Type. Type of construction is decided based on many factors such as insulation stress, mechanical stress, heat dissipation, weight, cost etc. Core and Shell form construction have their strengths and weakness depending on the kVA and kV rating. Most transformers today are made using core type construction.
Core Type Transformer: In core type transformer, the coils are wrapped around a core to form cylindrical shaped coils. High voltage winding are placed on the outside and the low voltage winding are placed on the inner side close to the core. This simplifies the problem of insulating the high voltage winding from the core.

Each phase has a single magnetic circuit with the core standing upright. Cross section of the transformer is circular. The mean length of winding turns is shorter (lower % impedance) in the core form construction while mean magnetic path is long compared to shell form. For moderate to large power transformers, core form construction is popular since the short circuit forces can be better managed with cylindrical type winding.
Most modern power transformers today are of core construction.
Shell Type Transformer: In shell type transformer, core is stacked around coil. Coils are usually flat or oval shaped with alternating high and low voltage windings. The coils are called pancake coils. Core is then assembled so as to encircle each side of the winding ring.
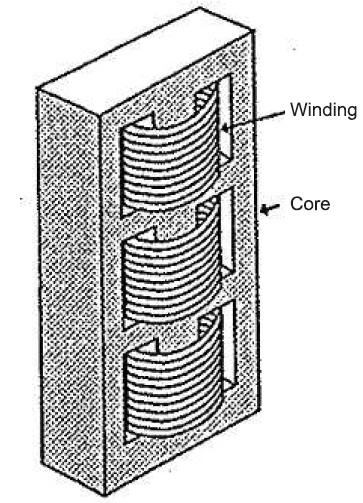
The mean length of winding turns is longer (larger % impedance) in the shell form construction while the mean magnetic path is shorter compared to core form. To make % impedance smaller the winding must be divided in to groups increasing the iron quantity. The cross section of a shell type transformer is square.
In larger sizes, shell form construction is quite appropriate. Winding and magnetic iron can be assembled on a steel base structure with lamination laid in horizontally to link and surround winding.
Core Vs Shell
Triplex Transformer and Tank Heating, Transformer Calculator, Transformer Open Circuit Test, Transformer excitation Current, Reactive Power of Transformer
[1]: IEEE C57.105, IEEE guide for application of transformer connections in three phase distribution systems.
