Data from power grid (utility) operators is often provided in one of the following formats at a given system voltage:
- Short circuit current, X/R ratio
- Short circuit MVA, X/R ratio
- Actual positive sequence impedance
Often times we need to convert from data in one format to another. This article details how to convert from one format to another and provides calculators that can handle this operation. Calculators are provided at the end of this article.
Basics
Here are some of the basics in per unit concept. The key is to understand that there are two main parameters that need to be known when dealing with per unit quantities. They are base voltage and base MVA.
Base Voltage (kVB): Often the supply voltage is used as the base voltage. If the power company delivery voltage is 13.2kV, the base voltage will likely be 13.2kV unless otherwise noted. Voltages are always line-line or phase-phase voltage.
Base MVA or Base kVA: A widely used base is 100MVA. But it is possible to select any other base if the operator chooses so.
1MVA=1000kVA.
kVA base, IB base current (A) and ZB base impedance(Ω) are given by following equations:
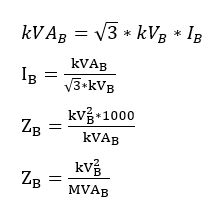
Now that the base parameters are defined let’s see how the per unit parameters are defined:
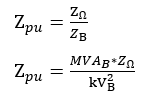
If the impedance is desired in actual ohms, the following formula can be used:

To convert short circuit current to MVA:
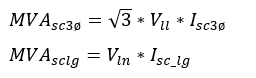
Where, Vll is the line-line voltage and Vln is the line-neutral voltage at which short circuit value is provided.
X/R Ratio Calculation
X/R ratio is the ratio of inductance to resistance of the power grid up to the point of fault. Near to large generating stations and large substations, this ratio will be high. At the tail end of long distribution lines and for low voltage systems the ratio will be lower. If the X/R ratio is 10, it means the inductance of the system is 10 times more than the resistance of the system.
X/R can be plotted on an impedance plane with R on the x-axis and X on the y-axis.
The hypotenuse of the triangle so formed gives the total impedance (Z) of the circuit. The various equations relevant to X/R ratio calculations are:
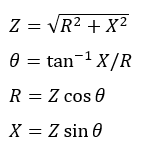
Refer to Sequence components if you need additional information on positive, negative and zero sequence parameters.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Short Circuit Current Conversion Calculators
Case1: Given Short circuit current (kA), X/R ratio
If data is available in this format, convert the short circuit current to equivalent short circuit MVA using the equations below.
![]()
Use line-line voltage and three phase bolted fault current for MVAsc3ø and line-neutral voltage and line to ground short circuit current for MVAsclg .
After converting to equivalent short circuit MVA use the calculator provided below in case 2 to obtain the utility impedance in R+jX format.
Case2: Given Short circuit MVA, X/R ratio
To get the short circuit parameters when the short circuit MVA and X/R ratio is provided use the calculator below.
Case3: Given positive and negative sequence impedance
To get the short circuit parameters when the positive and negative sequence impedance is given use the calculator below.
Additional Reading: Sequence Components
